India is a highly populated country with millions of internet users, it is one aspect of internet access and use. The second aspect contains the dark reality of unauthorized access to personal data due to the lack of standards and strict laws.
People who are using the internet are prone to losing personal information that they don’t even know. Here DPDP Act comes into play, this Act provides authority to the user to share, access, and erase their data with their consent.
What is the DPDP Act?
The DPDP full form is Digital Personal Data Protection 2023, it came into existence in August 2023. The aim of this Act is the protection of users’ data. This Act follows the PDPB Bill 2020. Here PDPB is the Personal Data Protection Bill, it focuses on creating a stronger data law in India. This act also introduces fines for breaking the data privacy rules.
The main purpose of DPDP is to ensure that personal data is handled in a way that respects people’s privacy while allowing for its legal use.
Why Was the DPDP Act Introduced?
The DPDP Act was introduced in India due to the rise in cases of personal data breach, misuse and data handling. India needed a comprehensive data protection law to handle these challenges:
Protecting People’s Privacy: Currently, people are using digital media for everything from banking transactions to studies. Their financial, medical, and biometric information is shared online daily. This makes it important to have some strict laws to protect these vulnerable data from unauthorized access to fraud and criminals.
Outdated Laws: Before the Act, India’s data protection laws were not enough to deal with modern data protection issues.
Automate your KYC Process & reduce Fraud!
We have helped 200+ companies in reducing Fraud by 95%
Brief History Behind the DPDP Act
Before 2022, India did not have a full privacy law. In 2017, the Supreme Court of India declared that privacy is a fundamental right in Puttaswamy’s judgment, also known as the Right to Verdict.
The court pointed out that India needs a comprehensive privacy law because the existing laws are not able to handle the privacy issues. After the verdict, the government worked on developing the data protection laws.
The earlier version of the Act including the DPDP Act 2021 was rejected and faced criticism. Then in November 2022, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology introduced the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, which replaced older laws including Section 43A of the IT Act and the SDRI Rules.
Who Is Covered Under the DPDP Act?
This Act covered the individuals and organizations that process personal data.
Individuals: The person who collects other personal data for specific purposes.
Organizations: These are companies, startups, and government bodies, that handle the personal data of people in India.
This Act is also applicable to international companies that collect and process the data of Indian citizens. These companies should have to follow the rules set by the Act.
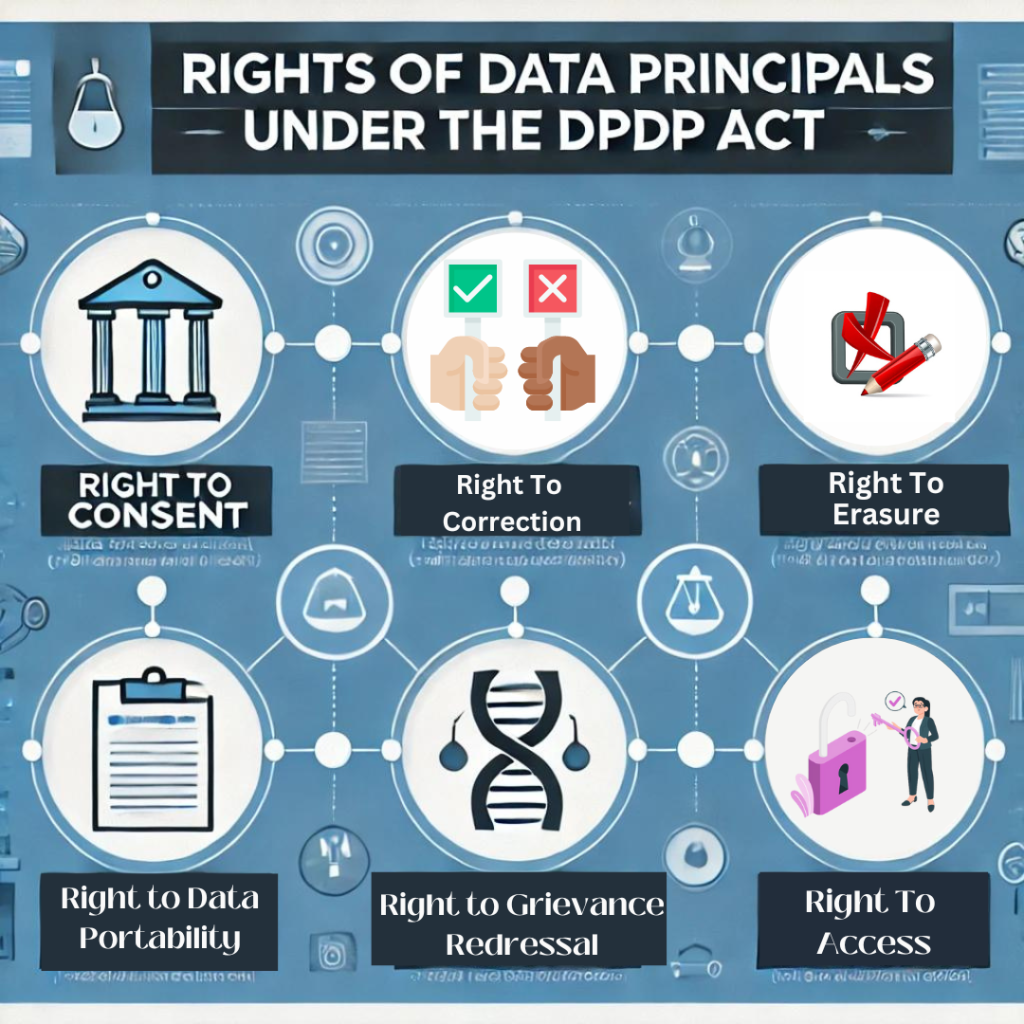
Rights of Data Principals Under the DPDP Act
The DPDP Act gives several rights to the Data Principals. Here the data principal refers to the person whose data is collected and stored. These rights are developed to give individuals control over their data. The Data Principals have these rights
- Right to Consent: Every data principal has the right to approve or disapprove the use of their data processing by the company. The company cannot process their data without consent.
- Right to Access: Individual has the right to know, what piece of their personal information are organizations using. They can ask the organization where they are sharing their data.
- Right to Correction: The data principal has the right to request the correction of inaccuracies or incomplete data by the organization.
- Right to Erasure: The Data principal has the right to request the organization to delete their data it is not mandatory or the individual has withdrawn consent.
- Right to Data Portability: Individuals can request organizations to transfer their data in a machine-readable format.
- Right to Grievance Redressal: Individuals can file complaints if they believe their data has been mishandled or their rights are violated.
Obligations of Businesses and Organizations under the DPDP Act 2023
Here are the key rules that businesses and organizations should follow:
- Obtain Consent: It is a must for the business to obtain the consent of the individual before collecting and processing their data.
- Data Minimization: Businesses can collect limited data that is necessary for the process. They should avoid excessive data collection.
- Data Breach Notifications: companies must inform the individual and DPDP board whenever a data breach happens.
- Security Measure: Organizations that are processing people’s data must use strong security measures. It is their responsibility to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
If the organization fails to protect the personal data of the Data principal, they might have to pay a penalty of 250 crore. The fine will be based on the severity of the violations. The business needs to follow the obligations of the Act if they do not want to face reputational damage and financial loss.
Conclusion
The DPDP ACT (Digital Personal Data Protection Act) is a revolutionary change in protecting personal data and ensuring individual privacy in India. According to it, the organization should get consent before using their data. It should keep the personal data safe and secure. The Organization should notify the individual and DPDP board if the data breach occurs. This Act gives power to the individual or data principal to have control over the data being processed and used. If the company fails to follow the obligation it will face penalties that can harm the reputation of the organization along with finance.
FAQs
1. What is the DPDP Act in India?
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act passed in 2023 focuses on the protection of the personal data of Indian citizens. It provides the right to an individual which lets them control their personal data sharing and processing and makes the data processing transparent.
2. What is the DPDP Act for Banks?
According to the Act, banks can collect and process personal data only for legal reasons, even if the person agrees to share personal information. If data usage breaks the law, it will be against the Act.
3. What is the DPDP Act full form?
The DPDP Act full form is the Digital Personal Data Protection Act.