Data is considered the most valuable asset. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a privacy law introduced by the European Union in May 2018. Its main purpose is to protect the personal data of individuals, just like DPDP in India. It reshapes how organizations handle privacy. Non-compliance with this law can lead to financial penalties and damage to reputation. Here, in this blog, you will learn about GDPR Compliance and why it’s important for businesses.
What is GDPR Compliance and its Full Form?
GDPR compliance refers to the application of the regulations and guidelines in GDPR. It refers to the implementation of rules and principles in the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
This law is intended to safeguard personal information and the privacy of people within the EU as well as the EEA (European Economic Area).
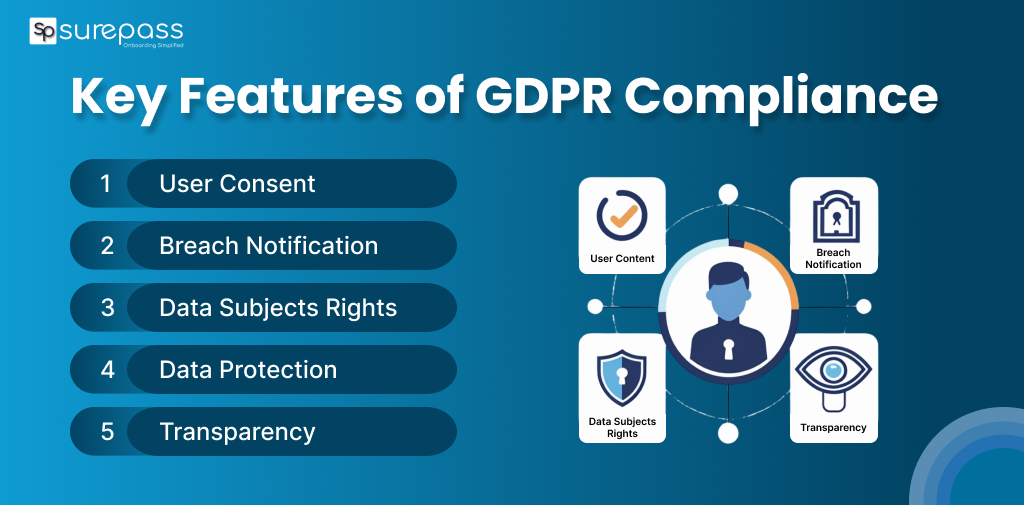
Key Features of GDPR Compliance:
- Reasons for Data Processing: A Business must have valid or legal reasons for collecting or processing personal information.
- User Consent: Businesses need to obtain user consent; they should state full information, not pre-tricked boxes.
- Data Subjects Rights: The users have rights to view and update their data, as well as delete it, and limit their use of data.
- Data Protection: Businesses need to protect their personal data by implementing appropriate protections (encryption and restricted access, and so on).
- Transparency: Clear and transparent privacy guidelines that explain how information is taken, stored, and employed.
- Breach Notification: If any personal information is compromised or leaked, officials and the affected persons are required to be notified within 72 hours.
- Reputation: Businesses should be able to prove that compliance with the GDPR (Records and Policies, as well as Personal Data Protection Representatives).
Automate your KYC Process & reduce Fraud!
We have helped 200+ companies in reducing Fraud by 95%
Key Principles of GDPR
The main purpose behind GDPR is to create a safe and unified digital market across the EU. These are key principles that businesses must know:
Transparency
People have the right to know how their data is being used. They must give clear consent before you process their data. Old data practices where people had to opt out, GDPR requires them to opt in first.
Even after giving consent, people can change their minds and withdraw it anytime. Companies also need to keep proper records, providing consent has been given.
Proportionality
You should collect the minimum data necessary for a specific purpose and keep it only for as long as required. The data must be accurate, updated, and protected from misuse.
Legitimate Purpose
Businesses must have a valid reason to collect and use personal data. Collecting unnecessary data.
GDPR allows data processing only under specific conditions, such as:
- To provide legal obligations (like a court order).
- To provide a service or product requested by the user.
- To protect someone’s interests (e.g., emergency medical care)
- To perform tasks in the public interest or under official authority.
- To pursue legitimate business interests – unless they conflict with people’s rights and freedoms.
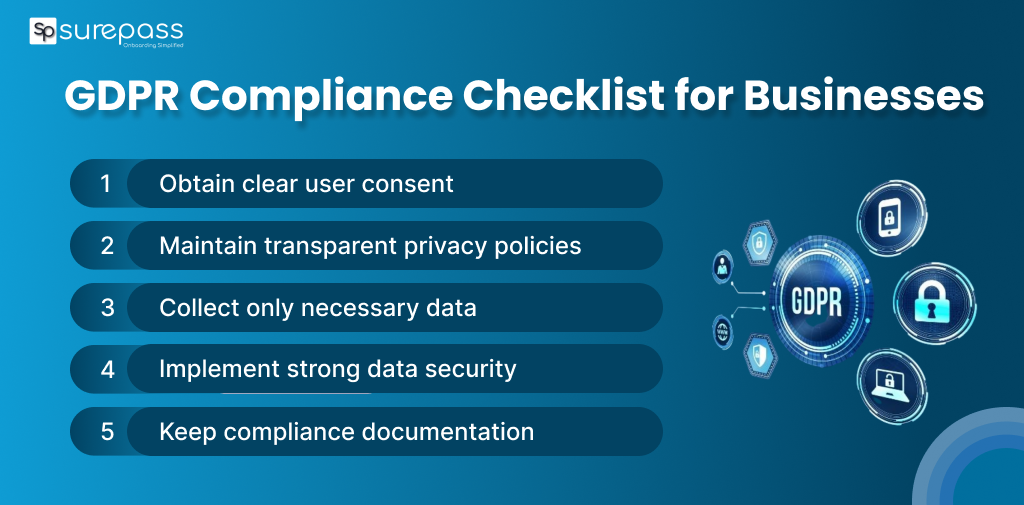
GDPR Compliance Checklist for Businesses
Here is the checklist that helps businesses comply with the law:
Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if required
If your business processes massive volumes of sensitive or personal information. Designating a Data Protection Officer (DPO) is crucial. The DPO serves as the principal individual responsible for monitoring the compliance of GDPR, overseeing internal procedures, training staff, and acts as the main point of contact.
Map Data Collection, Storage, and Usage
The business must have full visibility of the personal information it manages. It is about identifying the types of data being stored, including emails, names, or financial information, as well as where the data is stored.
Get User Consent for Data Processing
The law requires companies to obtain explicit consent from customers before taking their personal data. Consent forms must be easy as well as transparent and free of pre-checked boxes and hidden phrases.
Provide the Right to access, rectify, or erase data
Individuals have rights under GDPR. It can request access to their personal data, ask for corrections to inaccurate details, or request the complete deletion of their information. Businesses must follow users to share their data with another service provider.
Encrypt and Secure Personal Data
The protection of information goes far beyond documentation. Companies need to secure their sensitive information and restrict access using controls based on role, and frequently check security systems. Protecting against unauthorized access to breaches is among the main factors in GDPR compliance.
Ensure third-party vendors comply with GDPR
Numerous businesses rely on partners, vendors, as well as cloud service providers for processing personal information. The company’s role is to ensure the third party is legally compliant with GDPR. This is accomplished via Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) as well as regular inspections of the practices of vendors.
Report Data Breaches within 72 Hours
In case of a Data Breach, GDPR mandates that organizations report the data breach to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours. If the breach poses a high risk to individuals, those affected must also be informed without unnecessary delay.
Maintain Documentation of Compliance Practices
Keeping detailed records is a core part of GDPR. Businesses should maintain a Record of Processing Activities (ROPA), document logs, and update compliance policies regularly. Proper documentation not only proves compliance during audits but also ensures processes remain transparent and accountable.
GDPR Non-Compliance Fines
The severity of GDPR violations varies depending on the degree of violation. There are two levels of possible penalties. The maximum is EUR 10 million, or 2% of the global annual income for less serious violations, and as high as EUR 20 million, or 4% of annual global revenues. The penalty is determined through Data Protection Authorities (DPAs) in light of factors such as the severity of the violations.
Two Tiers of Fines
- Standard Maximum Penalty Up to EUR10 million, or 2percent of the company’s global revenue.
- Higher Maximum Penalty up to EUR20 million, or 4 percent of the total global revenue.
Why GDPR Compliance Matters for Businesses?
These are the main reasons why GDPR compliance is important for businesses:
- Builds Customer Trust
Our modern customer are more aware of their online privacy rights. When businesses comply with GDPR, it shows how customer data is collected or used. It builds trust, strengthens long-term relationships, and improves customer loyalty.
- Avoid Fines
If you fail to comply with GDPR can result in heavy penalties that can reach EUR20 million or 4% of worldwide turnover. By complying with the guidelines, businesses can prevent this loss.
- Improves Data Security and Brand Reputation
According to GDPR Compliance, businesses must follow strict data protection strategies, such as encryption, breach notification, and access controls. This builds trust and improves business reputation.
Conclusion
The GDPR’s compliance isn’t simply a list of regulations. It protects data from misuse. This is in accordance with the GDPR’s principles. It allows businesses to secure the privacy of sensitive information. This reduces the risk of data breach and prevents the ensuing sanctions. Beyond that, it promotes an cultural commitment and respect for the privacy of your customers.
FAQs
Ques: Is GDPR compliance mandatory?
Ans: Yes, GDPR compliance is mandatory for organizations.
Ques: How do I comply with GDPR?
Ans: Collect, process, and personal data according to rules and securely.
Ques: Does India have GDPR?
Ans: No, India does not follow the EU’s GDPR. It follows DPDP (Digital Personal Data Protection Act).
Ques: Which types of organizations need to comply with GDPR?
Ans: Any organization that processes, collects, or stores personal data needs to comply with GDPR.
Ques: What are the 6 legal bases of GDPR?
Ans: The 6 legal bases of GDPR: consent, contractual necessity, legal obligation, vital interest, public task, and legitimate interest.