Mobile Apps are the prime target for attackers. They find vulnerabilities and app logic. It helps them tamper with apps and reverse engineer. It is a threat to both the business and app users. The emulator detection helps find such devices and prevents further misuse. Detection ensures that only the real user can access and use the app features, rather than a fake virtual environment. It prevents tampering, data breaches of sensitive data, and automation.
What is an Emulator?
It is a software program that mimics another device or system. In simple words, it copies the hardware and operating system of devices so the app can run without the presence of a real physical device.
This process is known as emulation and emulation explained simply means mimicking or copying real device environment using software.
It is commonly used for app development, debugging, quality testing, and running legacy software. However, it can be misused for activities like fraud, reverse engineering, and automated bot attacks.
Automate your KYC Process & Reduce Fraud!
We have helped 3000+ companies in reducing Fraud by 95%
What is Emulator Detection?
It is a process used to identify whether an app is running on virtual devices created using an emulator or on a real device. Attackers use this device to bypass security controls, test exploits, or abuse.
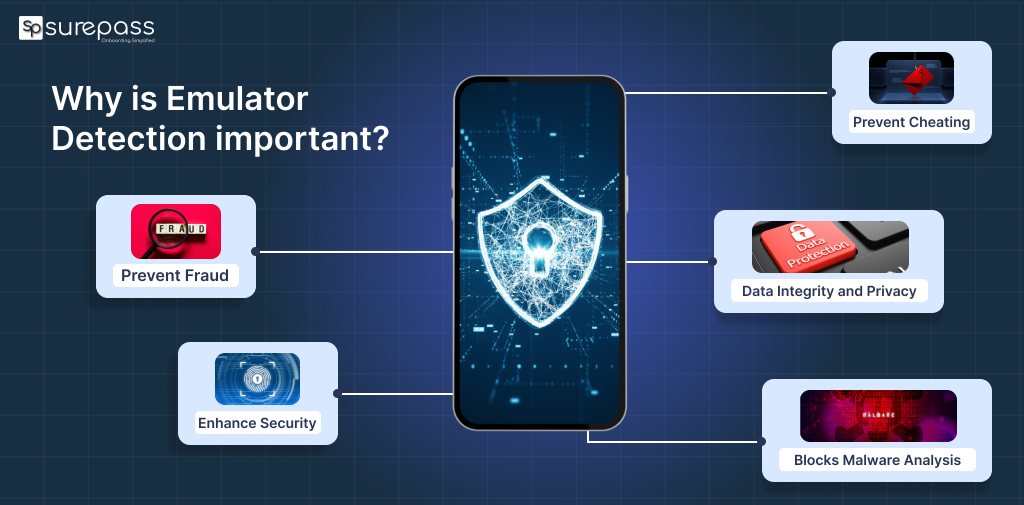
Why is Emulator Detection important?
It is important due to the following reasons:
- Prevent Fraud: Detection helps block fake installs, promotional abuse, and incentive fraud that inflate numbers and waste ad spend.
- Enhance Security: It helps block attackers from using emulators as a first step to reverse engineer code, attach debuggers, or tamper with apps.
- Prevent Cheating: It stops players from using memory scraping or GPS spoofing to gain unfair advantages.
- Data Integrity and Privacy: It protects sensitive user data from extraction and ensures analytics reflect real user behaviour and not bot activity.
- Blocks Malware Analysis: Malware analysts use emulators to study app logic. Detection makes dynamic analysis harder and protects intellectual property.

Common Android Emulator Detection Patterns
These are the common signs that help in detecting emulators:
- File and Directory Signatures
Emulators usually contain system files, directories, or packages that do not exist on real devices. Apps can scan for these emulator-specific artifacts. It is a common approach used in Android emulator detection.
- Unique Identifier Checks (IMEI, Serial)
Real phones have IMEI/serial numbers. However, emulators often return fake, null, or placeholder values (like all zeroes). It is a clear sign of virtualization.
- Hardware and Architecture Patterns
Emulators usually run on x86/x64 CPUs or have hardware names that don’t match with actual mobile chips. Apps can check CPU type to detect emulation.
- Resource and RAM Patterns
An imitator may exhibit unusual memory or RAM configurations that differ from those of typical real devices. Checking available RAM patterns can help.
- Performance or System Call Differences
It may respond differently to certain system calls or exhibit performance traits that differ from those of real hardware.
- Network/MAC Analysis
Some emulator network interfaces or MAC addresses look unusual. It is a hint of presence.
Best Tool for iOS and Android Emulator Detection
Surepass DeepID solution is best for detecting emulators. It uses various analysis and detection checks at the device layer to find suspicion. Emulator detection is one of its capabilities. It performs a check at run time and instantly confirms whether the device is real or a virtual mimic.
The real time and accurate analysis helps business take appropriate decision such as blocking emulators. It prevents risks of fraud and maintain secure environment.
Apart from the emulator detection, this standalone SDK offers other capabilities like Frida detection, Jailbreak/root detection, Promo code abuse control, GPS Spoofing, SIM Binding, etc. This is an all in one tookit designed for businesses for mobile app security.
What to do After an Emulator is Detected?
After detecting an emulator, apps must take preventive measures like blocking access to sensitive features, restricting account creation, and disabling rewards. It will prevent fraud without impacting the genuine users.
Industry Use Cases
Detection is essential for businesses handling sensitive personal and financial information of users.
- Banking and Fintech Apps
Emulators are used to reverse engineer financial apps and bypass security flows. It can result in financial loss and reputation damage. Here, detection protects sensitive transactions and customer data.
- Gaming Platforms
Many gaming players use emulators to automate gameplay, manipulate memory, or spoof location. Detecting such users ensures fair play.
- E-commerce and Reward-Based Apps
Fraudsters use emulators to farm promo codes, create fake accounts, and abuse referral rewards.
Conclusion
Emulator detection is not an option; it is a necessity for businesses to avoid fraud. As attackers are using emulation techniques to gain illicit benefits, timely detection is essential. It prevents sensitive data breaches, financial loss, user trust, and app safety. Deteting emulator requires many checks and reviews, such as file directory signature checks, unique identifier checks, RAM pattern checks, and more. These are common methods to find immitator. However, businesses cannot rely on a common method it needs a reliable device intelligence solution like DeepID.
FAQs
Ques: What is emulator detection in mobile apps?
Ans: It is a process of detecting whether an application is running in a real device or on a virtual environment.
Ques: Why do attackers use emulators?
Ans: Attackers use emulators to reverse engineer apps, automate actions, bypass security controls, create fake accounts, and conduct fraud without using real devices.
Ques: Can an emulator be detected?
Ans: Yes, emulators can be detected using detection tools or solution.
Ques: What is an emulator used for?
Ans: It is used to run and test apps or software without need of actual device.
Ques: Can emulator detection prevent reverse engineering?
Ans: Yes, emulator detection makes reverse engineering harder with blocking access after identification.
Ques: Can detecting an emulator stop automated bot attacks?
Ans: Yes, as in the identification business can block attacks.