Data Breach is a rising concern for people. Losing personal data of people is dangerous and causes reputational damage to businesses. Businesses must comply with DPDP regulations and process people’s data securely. The Data Principals will get the right to consent, access, correction, erasure, right to portability, and more.
If your business collects, processes, or stores user data, learning the role of Data Fiduciary is essential to avoid penalties.
What is Data Fiduciary?
Data Fiduciary means an individual or entity that determines the reason and method to process personal data. It is the responsibility of the entity to take technological, organizational, and security precautions to secure the personal data.
Who is Data Fiduciary?
Data fiduciaries are individuals and entities that decide the purpose and means of processing personal data. These entities are persons who decide how personal data is collected, stored, processed, and used.
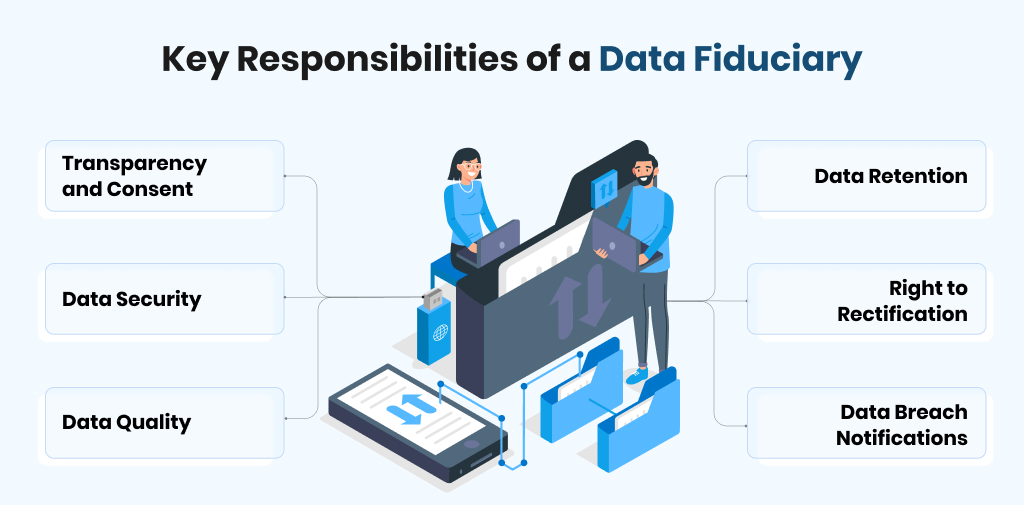
Key Responsibilities of a Data Fiduciary
- Transparency and Consent: Data Fiduciaries must inform data principals that their data is going to be used. They should obtain consent from the data principals before obtaining and processing their data.
- Data Security: They will be responsible for protecting personal data from unauthorised access, loss, or misuse.
- Data Quality: The Data fiduciary must ensure the data is accurate, complete, and updated.
- Data Retention: They must have the right to request a copy of their data in machine-readable format. They can ask copy of the format to transfer to another data fiduciary.
- Right to Rectification: Data principals also have the right to request principal update the incorrect data.
- Data Breach Notifications: They should immediately notify individuals about the Data Breach.
- Data Minimisation: Fiduciaries should collect and process the minimum amount of personal data necessary.
- Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): High-risk data processing activities, fiduciaries should conduct DPIAs to find and mitigate risks.
Automate your KYC Process & reduce Fraud!
We have helped 200+ companies in reducing Fraud by 95%
Best Practices for Data Fiduciaries
If you are an entity handling personal data, you must follow the DPDP rules. Here are the best practices:
- Implement Privacy by Design: Businesses should implement data protection into every stage of product/service development. They must minimise the data collection to only what’s important. Default settings should prioritise user privacy.
- Conduct Regular Audits and Risk Assessments: Do regular audits to identify vulnerabilities and integrate a high-security framework like VAPT (Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing).
- Prepare a Clear Data Breach Response Plan: Prepare yourself for an anti-data breach plan for immediate investigation and notifications.
What is Significant Data Fiduciary?
According to the DPDP Act, Significant Data Fiduciaries are the entities that handle a large volume of sensitive personal data. Companies are classified as SDF on the basis of data volume, data sensitivity, and risk of harm.
Extra Compliance Requirements for SDFs
- Appoint a DPO: They need to appoint a Data Protection Officer to monitor compliance and handle grievances.
- Conduct Annual Audits: Independent audits to evaluate data practices, with reports submitted to the Data Protection Board.
- Data Localization: It may face restrictions on transferring sensitive data outside India.
- DPIA Mandatory: Data Protection Impact Assessments for high-risk processing.
(Penalties for Non-Compliance: Up to Rupees 250 Crore)
Example of Data Fiduciary
- Large Fintech Companies: A Platform that processes a large volume of financial data (bank details, UPI Transactions, Credit Scores) and sensitive KYC information. They come under high-risk entities under DPDPA.
- Social Media Platforms: These platforms are used by millions of people in India. They collect user details, such as personal data, including messages, location, as well as the user’s behaviour. Because of the danger of data loss or misuse on these sites, the platforms fall under the Important Data Fiduciaries (SDFs).
- E-Health and Telemedicine Apps: These platforms store sensitive health information such as your medical history, prescriptions, and test results. This is critical personal data. According to the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA), this platform must follow stricter rules. It needs to keep the data safe using methods like encryption. Immediately informs users of a data breach and has limits on sending this data outside India.
- Credit Bureaus: These bureaus collect and manage sensitive financial information such as credit scores and loan history. This data affects a person’s ability to get loans or credit cards. According to DPDPA, these companies need to:
- Obtain clear consent before sharing anyone’s data.
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to handle data privacy.
- Take full responsibility for how personal data is used and protected.
Conclusion
Learning about the role of a Data Fiduciary is essential for businesses handling personal data. According Digital Personal Data Protection Act, the Data fiduciary must ensure transparency, obtain consent, maintain data accuracy, and protect user data with the highest standards of security. They are responsible for data breaches and fully accountable for how they manage personal information.
FAQs
What is Data Fiduciary?
Data Fiduciary is an entity or organisation that decides how the personal data will be collected, processed, or stored.
What is the difference between a data processor and a data fiduciary?
A data fiduciary decides how the individual data will be stored, collected, or used. While a data processor handles data on behalf of the fiduciary. It follows their instructions, but they can’t make decisions.
What is an example of a significant data fiduciary?
Fintech companies, banks, and E-commerce platforms are examples of data fiduciaries.