With the evolving technology, modern attackers are adapting new skills to bypass security. As businesses are relying on mobile apps for payment, onboarding, and data access. A rooted device is a threat to organizations like banking, fintech, insurance, and e-commerce. Understanding a rooted Android device is essential, along with knowing a root detector. It helps prevent fraud and unnecessary troubles for businesses.
What is a Rooted Device?
It is an Android smartphone or tablet, where users get control over the operating system by removing app restrictions. It gives administrator-level access to the users and allows changes to system files, settings, and apps. Rooting helps in customization, but it also weakens the device’s security. These devices become more vulnerable to malware, data theft, and fraud.
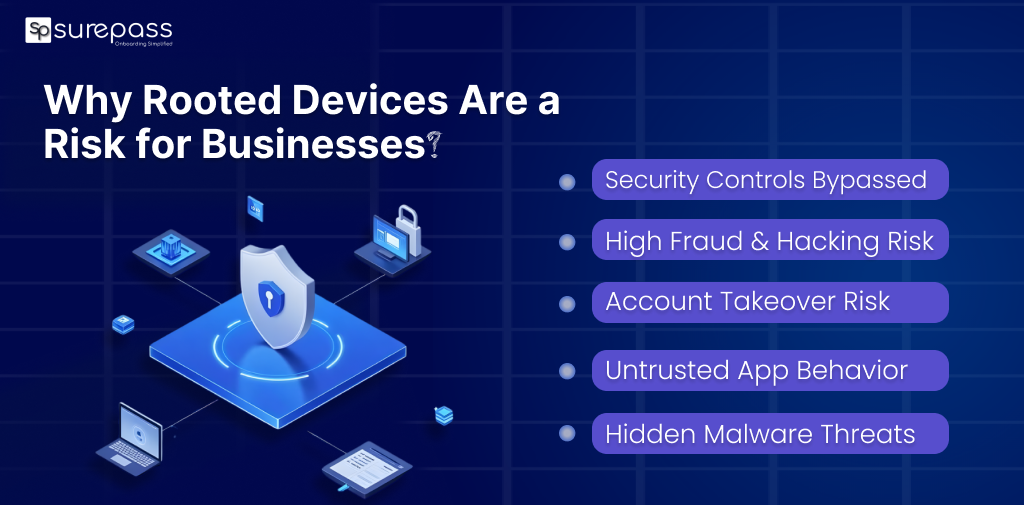
Why Rooted Devices Are a Risk for Businesses?
The devices are a threat to the business due to many reasons, such as:
- Security Controls can be Bypassed
Users can change system files. It means app security rules can be removed, disabled, and make the app unsafe.
- Higher risk of Fraud and Hacking
These devices allow fake apps, scripts, or tools run silently. Fraudsters can use root device to steal money, rewards, or sensitive information.
- Customer Data is not safe
A rooted device can be used to steal the sensitive personal or financial information of users from the app.
- Banking and Payment Apps can be manipulated
If a fraudster gains access on the root level, attackers can change the usual behaviour of payment apps, redirect transactions, or hide fraudulent activity from the system.
- App behaviour cannot be trusted
Apps can run in modified environments on such devices. Businesses cannot trust that the app behaves normally on such devices.
- Malware Can Run without Detection
These devices can hide malware inside the system. A normal antivirus solution may fail to detect or remove it.
- Increased risk of account takeover
Hackers can capture login details, OTPs, or session information. These data can lead to unauthorized account access.
- Violations of Security and Compliance Rules
Many industries require strong security controls. It allows a rooted device to break compliance standards and internal policies.
- Financial Losses and Chargebacks
These devices can result in refunds, money loss, and chargebacks for businesses.
- Loss of Customer Trust
Data breach or loss of customer-sensitive data can result in reputational damage.
Automate your KYC Process & Reduce Fraud!
We have helped 3000+ companies in reducing Fraud by 95%
Industries most affected by Rooted Device
A compromised device is a threat to various industries, including:
- Banking and Financial Services
These devices weaken built-in security controls. It makes bank apps vulnerable to credential theft, unauthorized transactions, and account takeovers. It increases the fraud and compliance risks.
- Fintech and Payment Platforms
Compromised devices can bypass security checks that can result in payment fraud, transaction manipulation, and higher chargeback rates.
- Insurance and Lending Apps
These devices allow attackers to tamper with data and identity manipulation. It allows users to exploit loan applications, submit false claims, or bypass risk assessment mechanisms.
- E-commerce and Digital Wallets
E-commerce and wallet based apps face threats like promo abuse, fake accounts, and payment fraud when accessed from rooted. It impacts revenue and customer trust.
How to detect a Rooted Device?
There are several methods for detecting a device whose operating system has been compromised. However, using a detection solution is essential. Businesses can use DeepID, a mobile app security and fraud intelligence system, to detect such devices.
It thoroughly analyzes a device with its advanced capabilities, like rooting detection, emulator detection, Frida detection, and more. It provides a risk score and rooted device detection signals and help business block this device.

Benefits of Rooted Device Detected Signal
There are many benefits of identifying a device with compromised root access:
- It helps businesses prevent fraud by identifying devices where security controls are bypassed, reducing unauthorized access and misuse.
- Protects sensitive customer information by blocking rooted devices that are more vulnerable to malware and data theft.
- Reduces financial losses and stops risky transactions initiated from compromised or manipulated Android devices.
- Enhance app security and ensure the application runs only in a trusted and secure device environment.
- Timely detection reduces the risk of account takeover fraud. It restricts access from rooted and tampered devices.
Conclusion
Mobile app security is essential for every business offering services online. Rooted devices are an issue for businesses. They remove system protections, making them easy targets for malware and fraud. A device with root access on user’s hand should be detected. A mobile app security solution like DeepID helps businesses identify such devices with its advanced device intelligence. DeepID helps businesses block compromised devices and prevent the unnecessary troubles that can occur.
FAQs
Ques: What is a rooted device?
Ans: It is an Android phone or tablet where the user has gained administrative privileges. The user has bypassed the built-in restrictions to access and modify core system files.
Ques: Are rooted devices safe?
Ans: No, It is not safe; it is vulnerable to malware, data theft, and system instability.
Ques: Is a rooted device good or bad?
Ans: It is bad for security -sensitive apps because it weakens system protections and increases the risk of fraud, data theft, and unauthorized access.
Ques: Can a rooted device be tracked?
Ans: Yes, they can be tracked using a root detection solution.
Ques: How to know if device is rooted?
Ans: Use DeepID to detect whether a device is rooted or not.
Ques: Is rooting a device illegal?
Ans: No, it is not illegal, but it is risky.