UIDAI aims to create a digital identity system that is built on a foundation of individual rights, privacy and minimum data collection. To help achieve this UIDAI has introduced a new way of verifying someone’s identity using Aadhaar where users share a copy of their digitally signed Aadhaar with the verifier, and the verifier then uses that digital signature to locally confirm that the identity provided is correct.
There are four official types of offline verification:
- Aadhaar Secure QR Code Verification
- Aadhaar Paperless Offline e-KYC (XML)
- e-Aadhaar Verification
- Aadhaar Verifiable Credential (VC) Verification
Let’s understand each one of them.
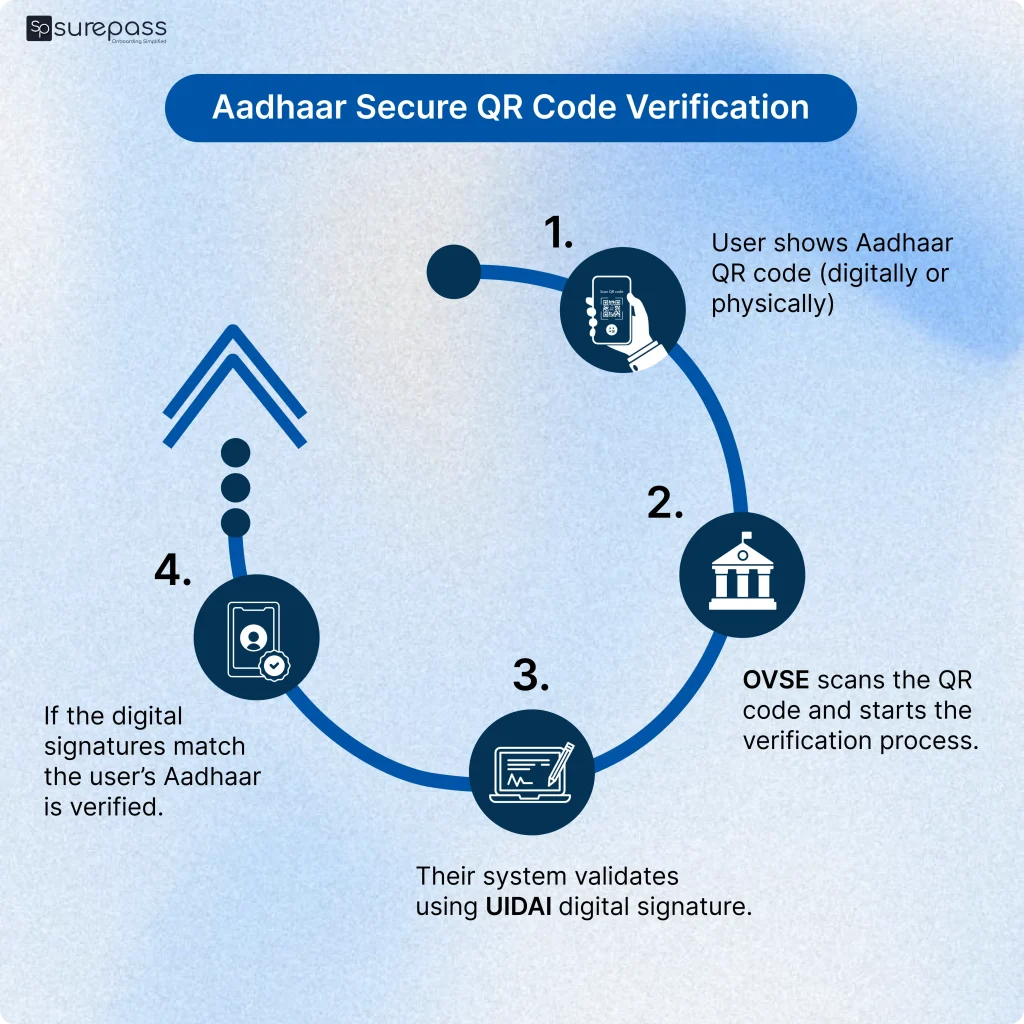
Aadhaar Secure QR Code Verification
This is the most widely used and simplest form of Aadhaar verification, where every form of aadhaar (PVC card, printed, e-Aadhaar, Aadhaar app) contains a digitally signed QR code which can be scanned for verification.
How it works
- User shows Aadhaar QR code (digitally or physically)
- OVSE scans the QR code and starts the verification process.
- Their system validates using UIDAI digital signature
- If the digital signatures match the user’s Aadhaar is verified
The QR code is tamper-proof because the signature breaks if modified
Where it’s used
- Hotel check-in
- Visitor entry gates
- Delivery verification
- Retail onboarding
Automate your KYC Process & Reduce Fraud!
We have helped 3000+ companies in reducing Fraud by 95%
Aadhaar Paperless Offline e-KYC
This is a shareable identity file instead of a scannable code. The user downloads an encrypted XML file from UIDAI which has the user’s demographic information and shares it with the OVSE along with a ‘share code’ for them to open the XML file.
How it works
- User downloads XML from the UIDAI portal
- The user shares the XML file and the ‘share code’ with the OVSE.
- OVSE opens the file and validates the data.
- Data is extracted by the OVSE.
Please note, unlike QR, this data can be stored (as per law).
Where is it used?
- Fintech onboarding
- SIM verification
- Insurance KYC
- NBFC onboarding
eAadhaar Verification
eAadhaar is a digital version of an Aadhaar card and can be downloaded in multiple formats, each file is password protected, digitally signed by UIDAI and has a secure QR code in it as well.
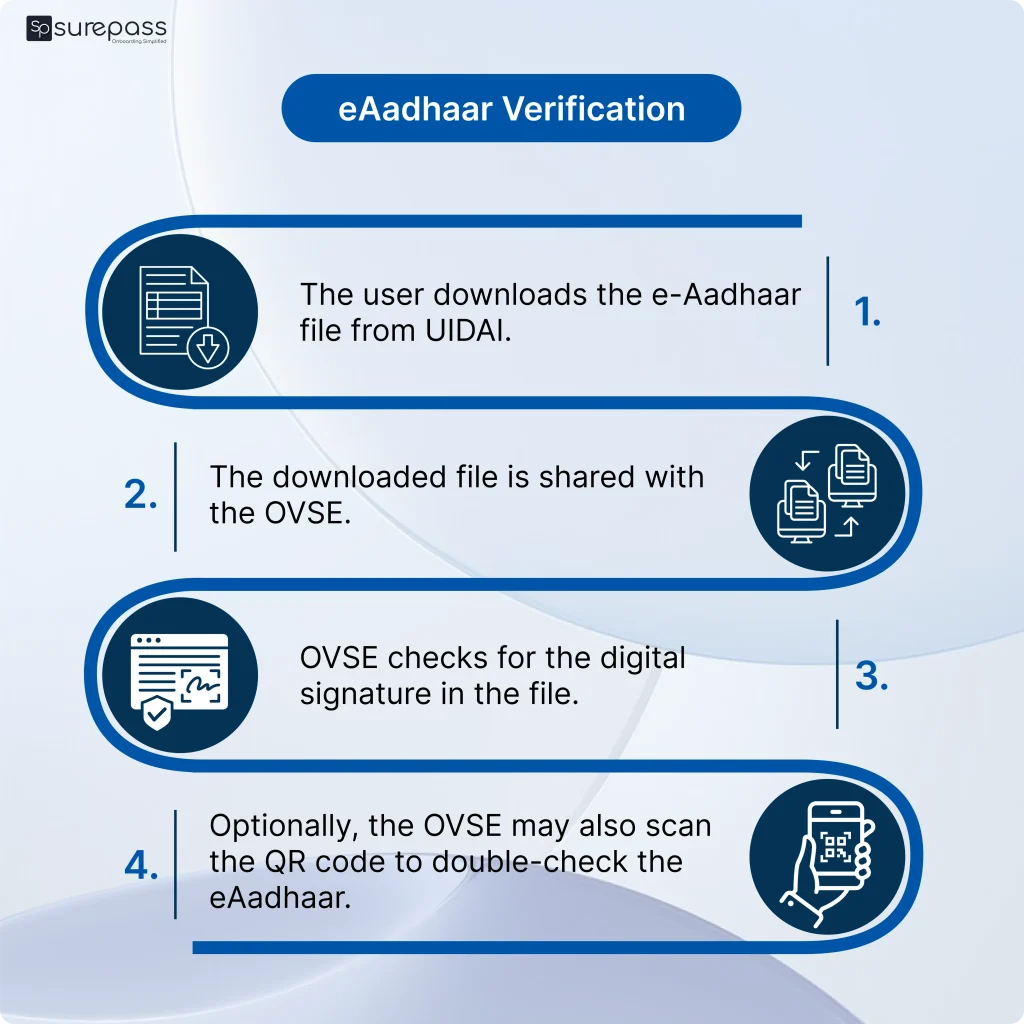
How does it work?
- The user downloads the e-Aadhaar file from UIDAI.
- The downloaded file is shared with the OVSE.
- OVSE checks for the digital signature in the file.
- Optionally, the OVSE may also scan the QR code to double-check the eAadhaar
Where is it used?
- Employee onboarding
- Government forms
- Rental agreements
- Education admissions
Aadhaar Verifiable Credential Verification
This is the future of Aadhaar verification. Instead of sharing documents, the Aadhaar App issues verifiable credentials stored in the user’s phone. The user shares only the required data fields that they select.
How it works
- OVSE requests the user for the credentials
- User approves request
- App shares signed credentials
- Verifier validates signature locally
Where it’s used
- Digital onboarding
- Access control
- Travel & events
- High-trust KYC
Please note that the use cases of this method are rapidly increasing.
Comparing Types of Aadhaar Offline Verification
| Method | User effort | Data shared | Storage allowed | Best for |
| QR Code | Show QR | Minimal | No | Physical presence checks |
| Offline XML | Share XML file | Full KYC | Yes | Fintech onboarding |
| e-Aadhaar | Share eAadhaar file | Full document | Sometimes | Formal verification |
| Verifiable Credential | Accept the request and send | Selective | Yes | Future digital identity |
Conclusion
Aadhaar Offline Verification lets businesses confirm identity without contacting UIDAI servers or storing the Aadhaar number. Instead, users share digitally signed details with their consent.
The four methods simply offer different levels of verification — QR code for quick checks, XML and e-Aadhaar for document-based onboarding, and Verifiable Credentials for sharing only specific data.
For companies, this means faster onboarding and less sensitive data to store. For users, it means better privacy because they share only what’s required. Overall, the system shifts identity verification from collecting copies of documents to sharing trusted proof of identity.
FAQs
Ques: What does Aadhaar Offline Verification Mean?
Ans: Aadhaar Offline Verification allows the identity verification of an individual without the need to connect to the servers of UIDAI. The individual presents identity information which is digitally signed and the verifier verifies the signature.
Ques: Does Aadhaar Offline Verification require access to my Aadhaar number?
Ans: No. Offline verification does not require the sharing and storage of the Aadhaar number. Only certain identity information voluntarily shared by the individual is provided.
Ques: Do I need to be connected to the internet to do offline verification?
Ans: No. Offline verification can be performed irrespective of having access to the internet to the UIDAI servers.
Ques: What are the different kinds of Aadhaar Offline Verification?
Ans: There are four major types.
Secure QR Code verification
Paperless Offline e-KYC (XML)
e-Aadhaar verification
Aadhaar Verifiable Credential (VC) verification
Ques: Can an enterprise retain the information obtained during offline verification?
Ans: This depends on the technique being used. With some techniques such as Offline e-KYC and Verifiable Credentials, retention is permitted, while for QR-based verification, retention is not permitted.
Ques: How is Verifiable Credential (VC) different from other methods?
Ans: Unlike methods that just use QR codes or fully share snapshots of documents, VC gives more control and privacy to its users. VC users have the ability to share specific attributes (e.g., just the age or name) without having to fully share identity documents.