With digitalization, everything has become so easy. We share our financial and sensitive data online. This data is vulnerable and can be misused. To prevent this, authentication and authorization methods are used. They ensure that the verified and authorized users can log in and access the service. However, people can get confused between these two terms. Here, in this blog, you will learn about these terms in detail.
What is Authentication?
It is a verification process in which a user, device, or system is verified before being permitted access to a resource. The verification confirms that user is genuine.
This process requires credentials such as a username and password, but modern systems also use biometrics (fingerprints, face ID), one-time passwords (OTPs), or Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for stronger security.
What is Authorization?
It is a process of deciding which user is allowed to do what within a system. It defines the level of access, resources, and actions that a user can perform after their identity has already been verified through authentication.
You can also understand these terms:
- Authentication = Who are you?
- Authorization = What is allowed to do?
Automate your KYC Process & reduce Fraud!
We have helped 200+ companies in reducing Fraud by 95%
Authentication vs Authorization: Key Difference
You have often heard about authentication and authorization. They may seem similar, but they serve different but complementary purposes.
| Aspect | Authentication | Authorization |
| Definition | User identity verification | Decides what the user can do |
| Question Answered | Who are you? | What can you access? |
| Process | First step of security | Second step, after authentication |
| Data Used | Username, password, biometric, OTP | Roles, permissions, and access rules |
| Visibility | User knows they are authenticating | Authorization is often invisible to the user |
| Example | Entering credentials to log in | Deciding if a user can access the admin dashboard |
Authentication vs Authorization: Examples
Authentication Example:
- Log in to your Gmail account with a username and password.
- Unlocking a phone with a fingerprint or face scan.
- Enter the One-Time Password (OTP) sent to your mobile.
- Using biometric scans at Airports.
Authorization Example:
- After logging into Gmail, only you can view your emails, not someone else’s.
- An employee logging into a company system can see only their own profile, while an HR manager can see all employee profiles.
- On a bank app, you may be able to check your balance, but not approve loans (only bank staff can).
- In streamlining service like Netflix, your child’s profile can only access kids’ content, while your profile has full access.
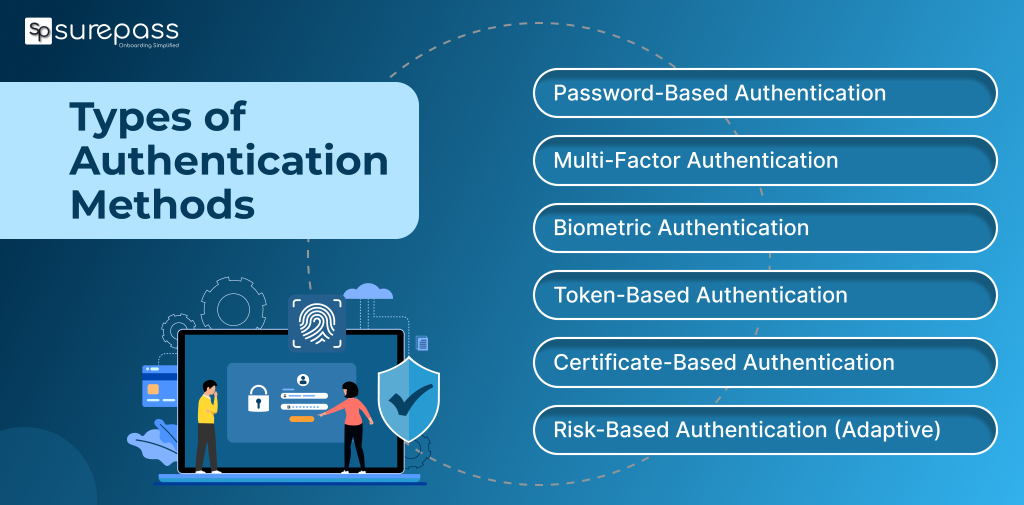
Types of Authentication Methods
These are some of the commonly used authentication methods that helps you differentiate between Authentication vs Authorization:
Password-Based Authentication
In this method, the user needs to enter the password and username. For example, logging into Facebook with your email + password.
- Pros: Most simple and widely used.
- Cons: A Weak password can be misused by hackers.
Multi-Factor Authentication
In this method, users need to verify themselves through two or more verification factors. Logging into the Gmail account with password+OTP.
- Pros: Secure method.
- Cons: Adds extra steps for users.
Biometric Authentication
This process involves unique biological traits for verification. For example, face scan, iris scan, and voice recognition.
- Pros: Hard to forge or seal.
- Cons: Needs special hardware: privacy concerns.
.
Token-Based Authentication
A digital token is generated after login and used to verify further requests. For example: Log in to the app, a session token (JWTm, OAuth token) is created to keep you logged in.
- Pros: Secure for web and mobile apps.
- Cons: Tokens can expire or be stolen.
Certificate-Based Authentication
This process used digital certificates to verify identity. For example: secure corporate VPN access with a client certificate.
- Pros: Very strong security.
- Cons: Managing certificates can be complex.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Only one set of credentials gives access to multiple applications. For example: Logging into Google and accessing Gmail, Drive, YouTube, etc.
- Pros: Convenient, as users don’t have to log in multiple times.
- Cons: If hacked, multiple apps are at risk.
One-Time Passwords (OTP)
It is commonly used to create unique and temporary passwords sent via SMS, email, or app. For example, OTP are sent by banks for online transactions.
- Pros: Stronger than static passwords.
- Cons: SMS/email OTPs can be intercepted.
Risk-Based Authentication (Adaptive)
You can adjust security requirements based on risk (location, device, behavior). For example, if you try to log in from a new country, the system asks for additional verification.
- Pros: Balances security and user experience.
- Cons: Needs advanced analytics.
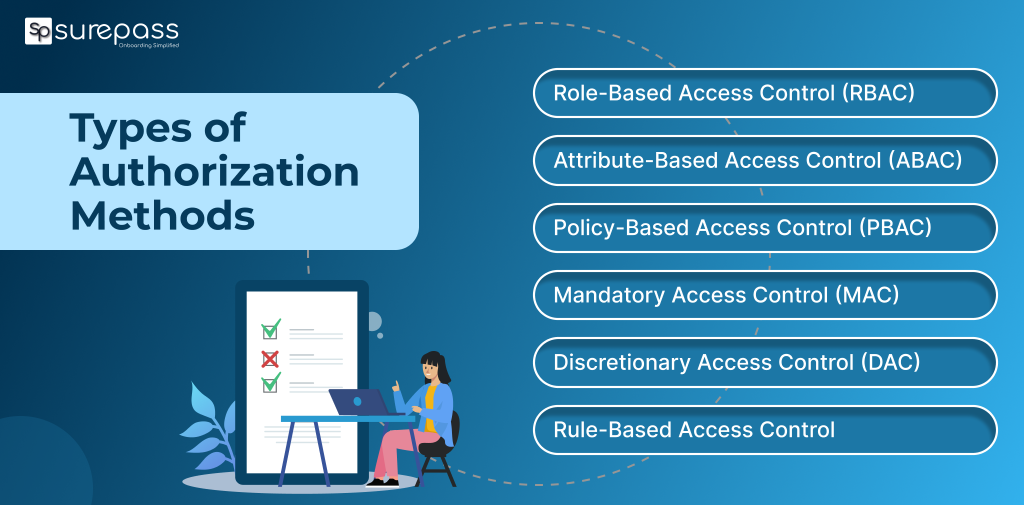
Types of Authorization Methods
These are commonly used authorization methods:
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
This is given based on the user’s role in an organization.
Example:
- An employee can view their own payroll.
- An HR manager can view all employees’ payroll.
Pros: It is easy to manage, especially for organizations with defined roles.
Cons: It is not flexible for complex scenarios.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
In this method, access is decided using multiple attributes (user, resource, and environment).
Example: A doctor can access patient records only during work hours and from hospital devices.
- Pros: Very flexible and fine-grained.
- Cons: Complex to set up and claim.
Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC)
It provides access control based on policies defined by the organization.
Example: Employees with proper security training can access sensitive data.
- Pros: It aligns security with business policies.
- Cons: Need strong governance.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
It is based on fixed classifications (security levels).
Example: Military System → Top Secret, Confidential, files, only users with matching clearance can access.
- Pros: It is the most secure and prevents unauthorized sharing.
- Cons: It is not user-friendly.
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
In this method, the data owner decides who can access the resources.
Example: In Google Drive, you choose who to share a file with (view, edit, and comment).
- Pros: Flexible and easy for users.
- Cons: Users may accidentally give access to the wrong people.
Rule-Based Access Control
Access is given according to the predefined rules.
Example: Firewall rules that allow only certain IP addresses to access a server.
- Pros: Simple and Straightforward.
- Cons: Too many rules make it complex.
Conclusion
The terms authentication and authorization seem similar. Both of these terms are related to verification but serve different purposes. People got confused between the terms authentication vs authorization. In simple words, authentication is verifying the user, and authorization is the process of giving access to the right user. These together ensure security, making it difficult for fraudsters to get access and preventing fraud.
FAQs
Ques: What is the difference between authentication vs authorization?
Ans: Authentication is about verification, and authorization is about giving access.
Ques: Is OTP authentication or authorization?
Ans: OTP is authentication.
Ques: What is an authorization and authentication API?
Ans: The Authentication API is a service that helps verify users, and the authorization is a service that helps access resources.
Ques: Which happens first, authorization and authentication?
Ans: Authentication comes first.
Ques: What type of authentication is SMS?
Ans: SMS is a type of two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication.